Screening
Screening for Cancer
Screening for cancer aims to pick up the disease at a stage when we intend to cure it.
Screening is done even without any symptoms being present.
People with a strong family history or personal history of cancer and other risk factors are usually offered screening and possibly genetic testing.
Women over the age of 35 years are subjected to a mammogram as a screening test for breast cancer.
For those with a high risk of breast cancer and in women younger than 35 years, Magnetic Resonance Imaging may be useful.
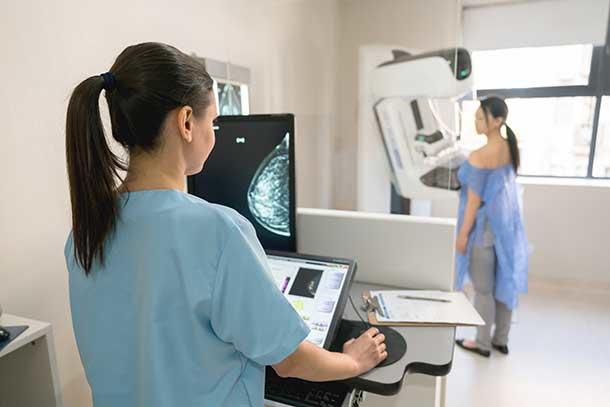
Mammography
The commonest screening tool for breast cancer is a mammogram. It is basically an X-ray of the breast tissue. A mammogram helps in finding tumors that are too small to feel. Factors that affect the probability of breast cancer detection are
A mammogram can pick up breast cancer before it has spread beyond the lining of the ducts (DCIS).
Its role is limited in younger individuals because they tend to have denser breasts and it becomes difficult to differentiate dense breast tissue from tumors.
Many factors affect whether mammography is able to detect (find) breast cancer
- NThe age and weight of the patient.
- NTumor size and type
- NLocation of tumor in the breast
- NSensitivity of breast to hormonal changes.
- NDensity of breasts
- NMammogram timing in relation to the menstrual cycle.
- NQuality of exposure in Mammogram
- NExpertise of radiologist to infer the findings.
Screening mammograms done in women aged 50-69years have reduced the chances of dying due to breast cancer than those who were not screened.
MRI is a screening tool where magnetic coils are used to generate images of the body and processed through computer algorithms to generate pictures of the body without the usage of X-rays
MRI is useful in screening for high-risk individuals like
Family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations.
- NGenetic Syndromes like Cowden/Li Fraumeni Syndrome.
- NStrong family history with first-degree relatives suffering from breast cancer.
- NRadiation treatment exposure during childhood.